Pentest Power Byte: Powershell, Bash, and Python
Are you prepping for CompTIA PenTest+ and getting tripped up by the scripting objectives? You’re not alone. Whether it’s a bash one-liner in a history file, a PowerShell snippet on a Windows host, or a small Python utility, being able to identify what you’re looking at and recognize risky patterns is essential for PT0-003.
That’s why I created the Pentest Power Byte series; it is a bite-sized, hands-on lesson that you can finish in 5–10 minutes. This module focuses on core skills like: tell which language a snippet is written in, spot indicators of malicious or suspicious behavior.
This is a series designed to help you pass Pentest 003. I know many of you are concerned that you are “not coders” and have had minimal exposure to coding. This post will help you identify the scripting languages that are testable objectives, show various outputs, and identify scripting errors.
Obviously, these are not REAL questions or examples from the exam, but this gives you ideas on how to start looking at the code and get you into the testing mindset for learning scripting languages.
Check out this free module: Pentest Power Byte: PowerShell, Bash & Python!
Lesson 1: Identify the Script Language
Exam Tips:
If you see
$UserandInvoke-Command, it’s PowerShell.
If you see#!/bin/bashorls, it’s Bash.
If you seedef,import, or indentation as syntax → Python.
Variables: same symbol, different meaning
$varappears in PowerShell and shells. Look for cmdlets (Get-,Write-Host) for PowerShell vs typical Unix commands for Bash.
Colons & indentation are Python flags
Missing
:afterdef/if/foror inconsistent indent = Python syntax error.
Python
requests,urllib,socket→ network activity (exfiltration or C2). Flag: network calls.subprocess,os.system,shlex→ runs shell commands (injection risk). Flag: unsafe execution.pickle,yaml(untrusted) → dangerous deserialization. Flag: remote code via data.paramiko→ SSH automation (lateral movement / persistence). Flag: remote access tools.
PowerShell
Invoke-WebRequest,Invoke-RestMethod,Start-Job→ downloads or background/network tasks. Flag: payload fetch / beaconing.New-PSSession,Enter-PSSession,Add-Computer→ remote execution / lateral movement. Flag: remote admin abuse.Import-Module ActiveDirectory, scheduling modules → account changes or persistence. Flag: privilege/persistence actions.
Bash / Shell
curl,wget,nc,socat→ pull payloads, reverse shells, or exfiltrate data. Flag: remote code / C2.cron,at,systemctl→ scheduled tasks or service changes (persistence). Flag: long-term access.
Lesson 2: Analyze for Malicious or Insecure Behavior
Below are exam-style snippets with the red flags CompTIA expects you to recognize.
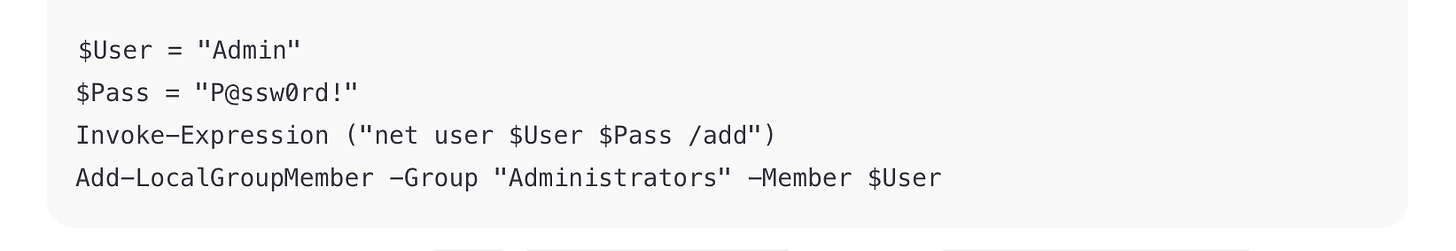
Example 1: Powershell
Identify: PowerShell (look for $Var, Invoke-Expression, verbs like Add-LocalGroupMember).
Malicious Behavior:
Adds a new admin account (
net user /add).Uses
Invoke-Expression— can run arbitrary code (RCE vector).
Exam takeaway: This is privilege escalation. Flag the use of Invoke-Expression and admin account creation.
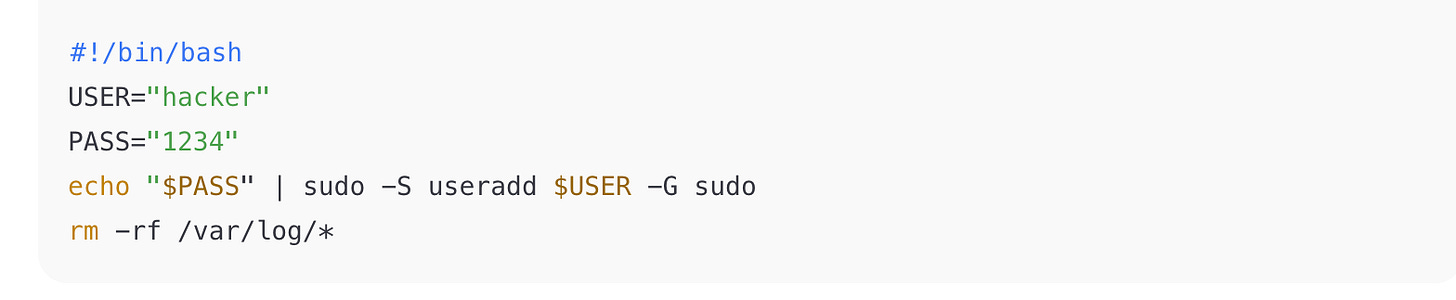
Example 2: Bash
Identify: Bash (shebang, sudo, rm -rf).
Malicious Behavior:
Creates a new sudo user with password fed via stdin.
Deletes
/var/log/*to hide evidence.
Exam takeaway: Recognize log wiping as anti-forensics and rm -rf as destructive.
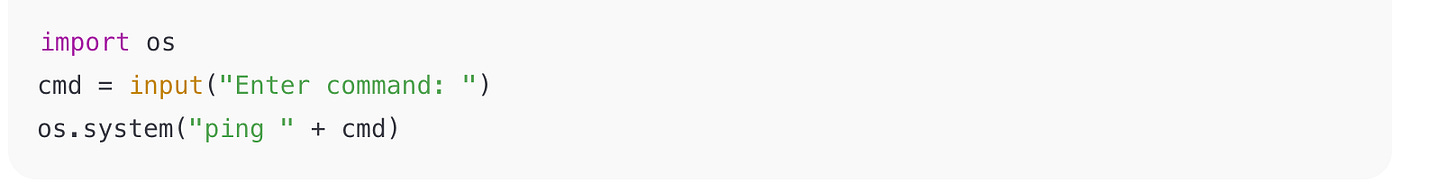
Example 3: Python
Identify: Python (uses import os, def, input).
Malicious/Insecure Behavior:
Unsanitized input concatenated into a system command = Command Injection.
Exam takeaway: Input validation failure → remote code execution.
Lesson 3: Identify Syntax or Logic Errors
It is important to recognize that some snippets are simply broken or misused, not obviously malicious.
Lesson 3: Example 1
➡️ Wrong Language Mix: $x with == belongs to PowerShell, not Bash.
Bash should use:
Exam takeaway: Recognize syntax inconsistencies that indicate the script won’t execute or has been tampered with.
Lesson 3: Example 2:
insert powershell
Lesson 3: Example 3
Insert python
Practice Questions (PT0-003 Style)
Question 1:
You discover the following script on a compromised Windows host:
Which of the following best describes the script?
A. Attempts to clean up temp files
B. Escalates privileges by creating a new admin user
C. Performs a network scan of local subnets
D. Attempts to install security updates
✅ Correct Answer: B — Privilege escalation by creating a new local admin.
Question 2:
What is the primary problem with this snippet?
A. os.listdir raises a NameError because os isn’t defined.
B. Missing colons (:) cause a SyntaxError.
C. print is used without parentheses (Python 3), causing a TypeError.
D. The for loop will run infinitely.
✅ Correct answer: B
Why: In this Python script snippet, both the def and for statements are missing the required trailing colon (:). That produces a SyntaxError before the code runs.
Fix (corrected snippet):
Exam tip: Look first for missing punctuation (colons, parentheses) when you see code that won’t parse.
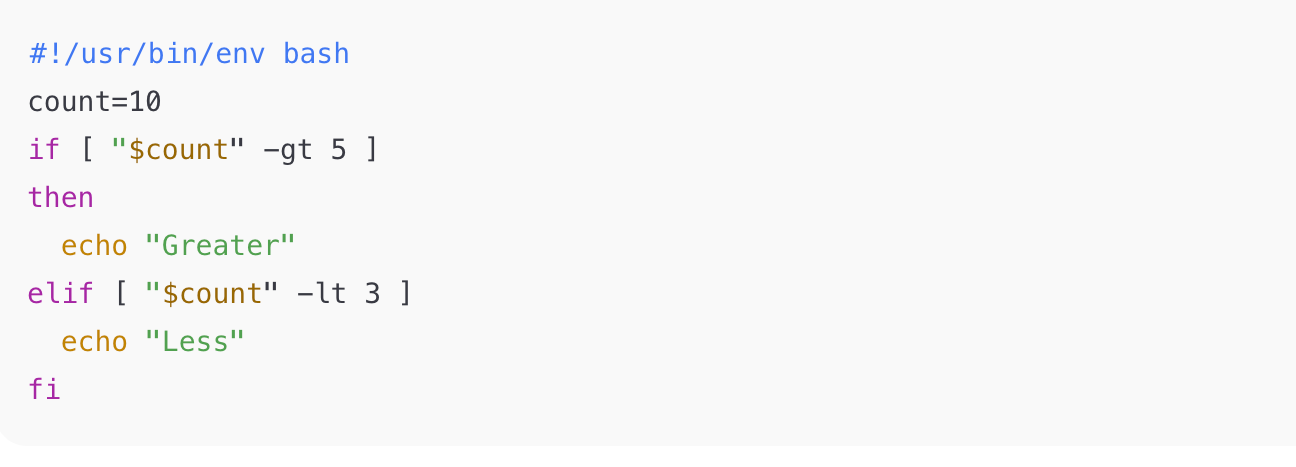
Question 3:
What is the primary problem with this snippet?
A. $count must be exported to use it in if.
B. -lt is invalid for numeric comparisons; -lt should be -le.
C. The elif line is missing a then, causing a syntax error.
D. echo cannot be used inside an if block without fi first.
✅ Correct answer: C
Why: The primary problem with this Bach snippit is the elif branch lacks the required then keyword (elif [ condition ] ; then). That results in a shell parse error. (Note: quoting “$count” is good practice — it avoids word-splitting if empty.)
Fix (corrected snippet):
In Conclusion
I hope this helps you in your studies. I wish you all the best of luck on the Pentest exam! If this helped you, let me know! Also, if you have suggestions for content or additions to this blog post that would be helpful, please don't hesitate to contact me.